Introduction: The Dawn of India’s Semiconductor Era
India is on the verge of a technological renaissance, with semiconductors at its core. Once a passive player in the global chip industry, India is now positioning itself as a formidable force in semiconductor manufacturing. This transformation is not just about industrial growth; it’s about reshaping the very fabric of our daily lives.
- 1. A Glimpse into the Past: India’s Semiconductor Journey
- 2. The Turning Point: The India Semiconductor Mission (ISM)
- 3. Strategic Collaborations and Investments
- 4. Technological Advancements and Innovations
- 5. Economic Implications: A Multibillion-Dollar Industry
- 6. Impact on Daily Life: From Smartphones to Smart Cities
- 7. Educational and Employment Opportunities
- 8. Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
- 9. Global Positioning: India’s Role in the Global Supply Chain
- 10. The Road Ahead: Challenges and Opportunities
- Conclusion: Embracing the Semiconductor Future
1. A Glimpse into the Past: India’s Semiconductor Journey
India’s foray into semiconductor technology dates back to the 1980s. Under the leadership of then-Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi, the country embarked on initiatives to bolster its electronics and semiconductor sectors. However, due to various challenges, including policy shifts and infrastructural limitations, India couldn’t capitalize on its early momentum .
2. The Turning Point: The India Semiconductor Mission (ISM)
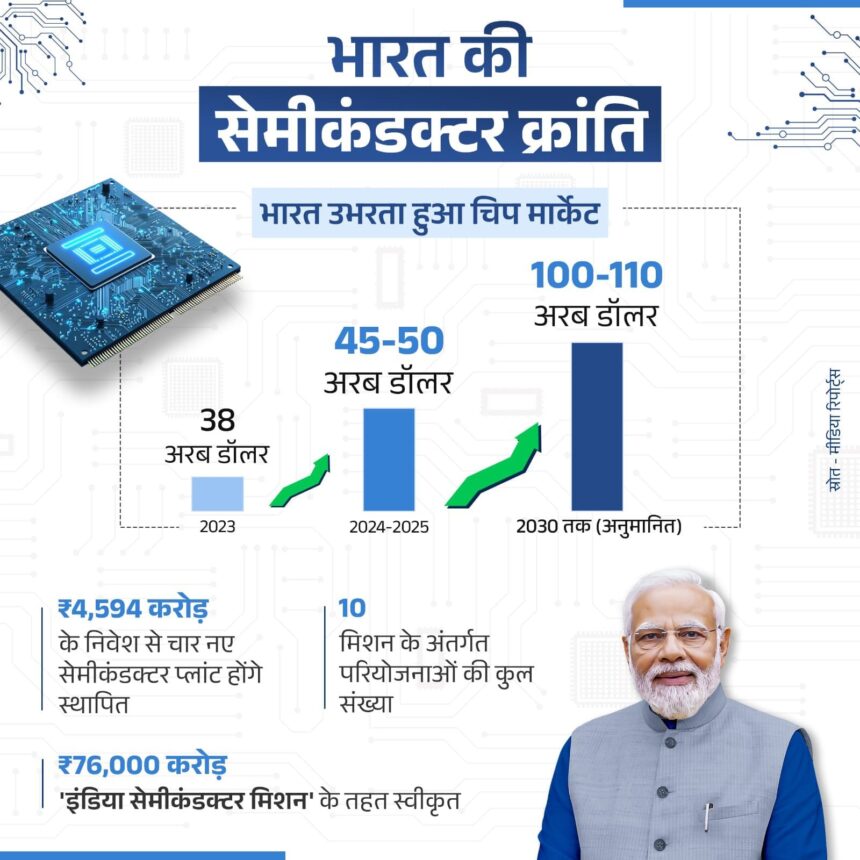
In 2022, the Indian government launched the India Semiconductor Mission (ISM), a transformative initiative aimed at establishing a robust semiconductor manufacturing ecosystem. With an investment of $10 billion, the mission seeks to promote domestic production, reduce dependency on imports, and position India as a global semiconductor hub .
3. Strategic Collaborations and Investments
India’s semiconductor aspirations have garnered international attention. Collaborations with global giants like Micron Technology are paving the way for advanced chip manufacturing in the country. Additionally, the establishment of semiconductor fabrication units in states like Odisha and Punjab underscores India’s commitment to this sector.
4. Technological Advancements and Innovations
The focus isn’t solely on manufacturing; India is also making significant strides in semiconductor research and development. Institutions like the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) are at the forefront, working on cutting-edge technologies such as gallium nitride (GaN) and silicon carbide (SiC) chips, which are pivotal for electric vehicles, renewable energy, and defense applications.The Times of India
5. Economic Implications: A Multibillion-Dollar Industry
The semiconductor sector is poised to become a cornerstone of India’s economy. With projections estimating the market’s value to reach $271.9 billion by 2032, the industry promises substantial economic growth, job creation, and enhanced technological capabilities .
6. Impact on Daily Life: From Smartphones to Smart Cities
Semiconductors are the unsung heroes behind many of the technologies we use daily. From smartphones and laptops to smart home devices and automobiles, chips are integral to their functionality. A thriving domestic semiconductor industry ensures better availability, affordability, and innovation in these products, directly enhancing the quality of life.
7. Educational and Employment Opportunities
The semiconductor revolution is creating a surge in demand for skilled professionals. With India’s vast pool of engineering graduates, there’s a significant opportunity to train and employ individuals in semiconductor design, manufacturing, and research. This not only addresses the industry’s talent needs but also contributes to the nation’s human capital development.
8. Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
As India ramps up semiconductor production, there’s a concurrent emphasis on sustainable practices. Efforts are being made to adopt energy-efficient manufacturing processes and recycle materials, ensuring that the growth of the semiconductor industry aligns with environmental conservation goals.
9. Global Positioning: India’s Role in the Global Supply Chain
India’s entry into semiconductor manufacturing is strategically significant. By diversifying the global supply chain, India aims to reduce geopolitical risks and establish itself as a reliable partner in the technology sector. This move enhances India’s influence in global technological affairs and fosters international collaborations.
10. The Road Ahead: Challenges and Opportunities
While the prospects are promising, challenges remain. Issues related to infrastructure, skilled workforce, and technological gaps need to be addressed. However, with continued investment, policy support, and international partnerships, India is well-positioned to overcome these hurdles and lead in the semiconductor domain.
Conclusion: Embracing the Semiconductor Future
India’s semiconductor revolution is more than just an industrial shift; it’s a testament to the nation’s resilience, innovation, and vision for the future. As semiconductors become increasingly integral to our daily lives, the advancements in this sector promise a future where technology serves as a catalyst for societal progress and well-being.
FAQs
Q1: What is the India Semiconductor Mission (ISM)?
The ISM is a government initiative launched in 2022 with an investment of $10 billion to promote semiconductor manufacturing in India.
Q2: How will the semiconductor industry impact daily life?
Advancements in semiconductor technology will lead to more affordable and innovative electronic devices, enhancing the quality of life.
Q3: What are the environmental implications of semiconductor manufacturing?
Efforts are being made to adopt sustainable manufacturing practices, ensuring minimal environmental impact.
Q4: How can individuals contribute to the semiconductor ecosystem?
Pursuing education and careers in semiconductor-related fields can contribute to the industry’s growth and innovation.
Q5: What is India’s global strategy in semiconductor manufacturing?
India aims to diversify the global supply chain and establish itself as a reliable partner in the semiconductor sector.