7 Eye-Opening Truths About Radiography That Are Changing Modern Healthcare
Radiography, often underestimated, is the unsung hero of modern medicine. Whether it’s detecting a broken bone, diagnosing pneumonia, or helping in cancer detection, radiographic imaging is a foundational pillar of diagnostics. This article explores the history, key facts, significance, side effects, observance, timeline, and societal impact of radiography in a warm, human-centered style.
- 🔮 What is Radiography?
- 🕰️ Timeline: Evolution of Radiography
- 💡 Key Facts About Radiography
- 🌍 Significance of Radiography in Society
- 🚫 Risks and Safety Concerns
- ✨ Importance in Our Lives
- 😊 Human Behavior and Radiography
- 🙏 Wishing Wellness and Appreciation
- 🚀 Daily Life Impacts of Radiography
- ❓ FAQs About Radiography
- 🌟 Conclusion: Radiography is a Silent Revolution
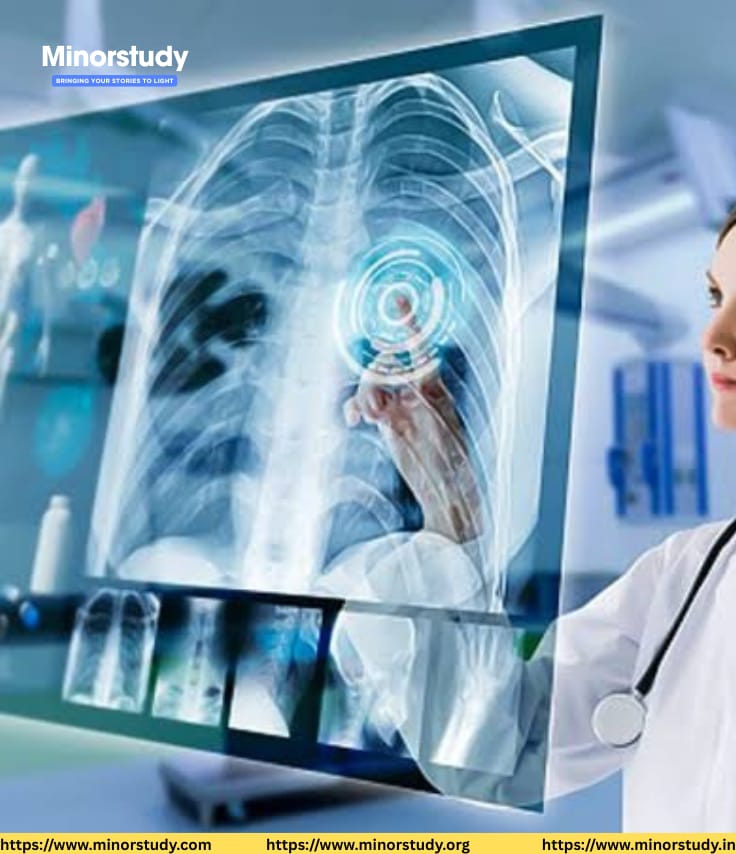
🔮 What is Radiography?
Radiography is a medical imaging technique that uses X-rays to view the internal structures of the body. The images produced are called radiographs. Trained professionals called radiologic technologists or radiographers perform the procedure under physician supervision.
Radiography includes:
- Conventional X-rays (e.g., chest, bones)
- Computed Tomography (CT)
- Fluoroscopy (real-time imaging)
- Mammography (breast imaging)
🕰️ Timeline: Evolution of Radiography
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1895 | Wilhelm Röntgen discovers X-rays |
| 1896 | First medical X-ray performed |
| 1913 | Coolidge tube developed, enabling safe use of X-rays |
| 1972 | CT scans introduced by Sir Godfrey Hounsfield |
| 2000s | Digital radiography becomes mainstream |
| 2020s | AI integration in radiology and image analysis |
💡 Key Facts About Radiography
- Non-invasive: Radiography is typically quick and doesn’t require surgery.
- Painless: Except for positioning, the procedure itself causes no pain.
- Radiation dose varies: Most routine X-rays expose you to minimal radiation.
- Crucial in emergencies: It’s the first diagnostic tool in trauma and ER settings.
- Used in dental, orthopedic, cancer, and cardiac care.
🌍 Significance of Radiography in Society
Radiography helps doctors:
- Diagnose fractures, infections, tumors, and foreign bodies
- Guide treatment and monitor progress
- Detect early signs of diseases
- Reduce the need for exploratory surgeries
Its ability to save lives by early diagnosis makes it indispensable.
🚫 Risks and Safety Concerns
Although radiography is widely safe, it’s important to be aware:
- Radiation exposure, though low, can be harmful in excess.
- Pregnant women are generally advised to avoid X-rays unless necessary.
- Repeat exposure should be monitored.
Technological advances like digital X-rays and low-dose protocols have made radiography significantly safer.
✨ Importance in Our Lives
Radiography impacts us more than we realize:
- Early cancer detection (e.g., mammograms)
- Post-surgery healing checks
- Pediatric care without invasive procedures
- Dental exams that prevent long-term decay
It also reduces healthcare costs by preventing major interventions through early action.
😊 Human Behavior and Radiography
For many patients, an X-ray visit is their first hospital experience. It can be:
- Intimidating due to unfamiliar machines
- Emotionally stressful while awaiting results
- Relieving when diagnosis brings clarity
Radiographers play a huge role in reducing anxiety by being warm, clear, and professional.
🙏 Wishing Wellness and Appreciation
- ❤️ “To every radiographer: your quiet role saves loud lives.”
- ✨ “Wishing patients clarity, courage, and comfort in every scan.”
- ☕ “May technology serve healing and human touch continue to comfort.”
🚀 Daily Life Impacts of Radiography
- Improves diagnosis speed
- Enables remote consultations through digital radiographs
- Boosts confidence in treatment plans
- Shortens hospital stays due to precise diagnosis
❓ FAQs About Radiography
Q1: Is radiography painful?
No. Except for positioning, it’s usually painless.
Q2: How long does it take?
Most X-rays are done in 10–20 minutes.
Q3: Can children get X-rays safely?
Yes, with adjusted dosage based on age/weight.
Q4: Can X-rays detect everything?
No. Some soft tissues or small abnormalities may require other scans (MRI/CT).
Q5: What about radiation exposure?
Minimal in most cases; modern machines use lower doses.
🌟 Conclusion: Radiography is a Silent Revolution
While radiography may not grab headlines, its life-saving role cannot be overstated. It empowers doctors, comforts patients, and advances medicine silently but powerfully.
As technology and humanity evolve, so too will radiography—bridging the gap between machines and miracles.