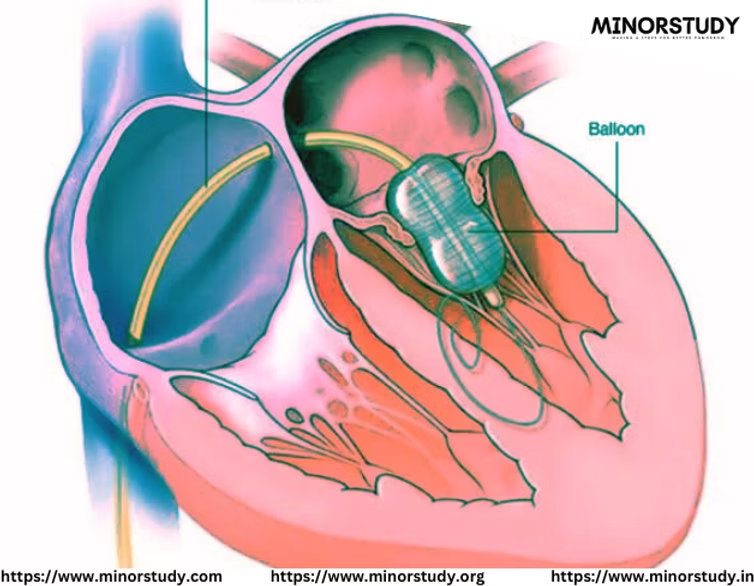
PTMC (Percutaneous Transluminal Mitral Commissurotomy)
PTMC is a minimally invasive medical procedure used to treat mitral stenosis, a condition where the mitral valve of the heart becomes narrowed. This procedure improves blood flow by widening the mitral valve without the need for open-heart surgery.
Indications for PTMC
Severe mitral stenosis with symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and heart palpitations.
Rheumatic heart disease, the most common cause of mitral stenosis.
Pulmonary hypertension due to mitral valve narrowing.
Asymptomatic mitral stenosis with a high risk of complications, such as during pregnancy.
Procedure Overview
Step | Description |
Pre-procedure Assessment | Echocardiography and imaging studies are performed to evaluate the mitral valve anatomy. |
Local Anesthesia | The patient is given local anesthesia or light sedation. |
Catheter Insertion | A catheter is inserted through a vein (typically in the groin) to reach the heart. |
Balloon Inflation | A balloon-tipped catheter is guided to the mitral valve and inflated to widen it. |
Monitoring | Continuous imaging (fluoroscopy or echocardiography) ensures accurate placement. |
Completion | The balloon is deflated and removed after achieving proper valve opening. |
Advantages of PTMC
Minimally Invasive: No need for open-heart surgery, leading to quicker recovery.
Effective: Improves blood flow and reduces symptoms of mitral stenosis.
Shorter Hospital Stay: Patients can often return home within 1–2 days.
Suitable for High-Risk Patients: Especially beneficial for individuals who cannot undergo surgery.
Risks and Complications
While PTMC is generally safe, potential risks include:
Bleeding or infection at the catheter insertion site.
Mitral regurgitation: Leakage of the valve after dilation.
Arrhythmias: Abnormal heart rhythms during or after the procedure.
Stroke: Rare but possible due to embolism.
Post-Procedure Care
Monitoring: Regular follow-up with echocardiography to ensure valve function.
Medications: Anticoagulants or antibiotics to prevent blood clots and infections.
Lifestyle Changes: Maintaining heart health with a balanced diet, exercise, and avoiding tobacco.
Why PTMC is Important
Life-Saving: Restores normal blood flow and prevents complications like heart failure.
Pregnancy-Safe: Often preferred for pregnant women with severe mitral stenosis.
Improved Quality of Life: Relieves symptoms and enhances daily functioning.
PTMC has revolutionized the treatment of mitral stenosis, offering patients a safer and less invasive alternative to traditional surgery.